Windows Registry Backup
Every time you install a new application on your Windows computer, the application will most likely make changes to a huge application database called the "Windows Registry". Think of the Windows Registry as a large collection of application and system settings and configurations. When the Windows Registry is in decent health, Windows is happy and runs smoothly.
When the registry is corrupted, Windows might run sluggishly, not boot up correctly, or crash unexpectedly. It just takes one poorly written program (or malware) to wreak havoc on the Registry. The best line of defense would to make a backup of the Registry so that you can easily restore it should it ever become unstable or corrupted by a bad piece of code.
Registry Backup on Windows 7
The Registry is a big, scary beast but backing it up is a remarkably easy task. You will not even need administrative access to backup your Registry. In the Windows Start menu type in "regedit" and the handy Windows registry editor will fire up.
When viewing the Registry for the first time, you might be tempted to drill down the drop-down lists and do some exploring but be careful that you don't inadvertently delete or create any new Registry entries. It's best to leave it alone.
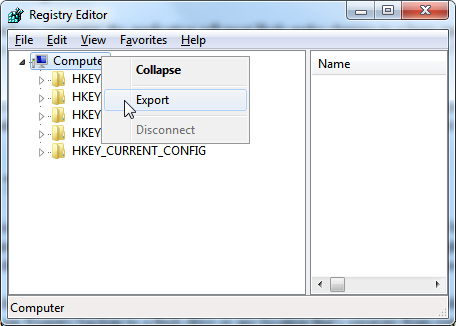
Go to the very top to the Computer icon and right click on it. In the right-click context menu select "Export". Navigate to a folder to save your Registry backup to in the "Export Registry File" dialog box. It's a good idea to save your Registry backup to a flash drive or any location that's separate from your main Windows disk.
Windows Registry Editor
Simple Registry Backup
The Windows Registry is huge database of application and system settings. When it becomes unbalanced, Windows may become cranky and not operate optimally. The more applications you install, the higher the chance of the Registry becoming corrupted.
The effects of a corrupted Registry range from random reboots to distressing system freezes. When your Windows computer is running as you like it, make a backup of the Registry so that you can restore your system to its old self should the Registry become unstable.